Search engine optimization, commonly known as SEO, is an essential tactic used by digital marketers and online businesses alike. It is the process of improving the on-page and technical aspects of a website so that it performs well in search queries and delivers organic traffic.
There is so much demand for visibility online today that without optimizing for search engines, your website may simply not get found. There is, however, a misconception that you have to be an expert to do SEO. Luckily, that's not the case, and in this article we'll show you how to do your own SEO.
Table of Contents
How SEO Works
Search engines like Google want to provide only the best and most accurate results to a search query. As a result, they crawl all the content on the web and index everything, like a library of books. When your content fits a search query, it will be displayed in the results – and the better the fit, the higher up in the list it will appear.
The SEO process involves a collection of steps aimed at making a website more search engine-friendly but also user-friendly. Keywords are integrated into the content to help search engines understand and find the right web pages. Then technical SEO ensures that the website's structure, speed, and security meet search engine standards.
SEO: Key Factors
Search engine optimization will include most, if not all, of the following key features:
- Keyword optimization – Specific researched keywords that form the focal point of a search query.
- Meta title – This is displayed in the SERPs and is integral for attracting attention and getting clicks.
- Meta description – This is less important for SEO but does explain to the user what the page is about and can therefore encourage them to click the link.
- Heading tags – Headings are used throughout the content as a way to break up the text and make it scannable for readers. Heading tags are the HTML code that tells search engines about the structure of your headings.
- Image optimization – Large images will slow page loading speeds, so images must always be compressed to avoid this.
- Quality content – The best content is engaging, easy to read, and answers a question or provides value in some other way.
- Internal linking – This is a great SEO practice that develops a network across your pages and helps a search engine index related pages on your site. It also works to keep an engaged reader on your site longer.
- Backlinks – Backlinks from other sites to your site show credibility and are highly rated by search engines, though they can be elusive to acquire.
- Social widgets – These handy buttons enable sharing to different social media platforms, which is a bonus for SEO and helps promote your content in other places.
- Schema markup – Adding schema markup is yet another way to help search engines read and understand your content. It also allows rich snippets to be created from your content and displayed in the search results.
- Optimized URLs – Long URLs are bad for SEO.
The Process of Search Engine Optimization
The process of search engine optimization can be broken down into three separate aspects: on-page SEO, technical SEO, and additional extras. When developing content, using a blogging platform like DropInBlog means you’ll have all the SEO functionality you need to get better rankings.
On-Page SEO
1. Keyword Optimization
Start with conducting keyword research based on words or phrases you think customers will be searching for. Make use of a keyword research tool like Ahrefs or Wordstream. These will show you all the metrics you need to select the best keywords to target.
When selecting keywords, look for those with a high search volume and a low difficulty score. Those words that have a low difficulty score have less competition and are easier to rank for. If they also have a high search volume, that means a greater chance of more traffic for your site.
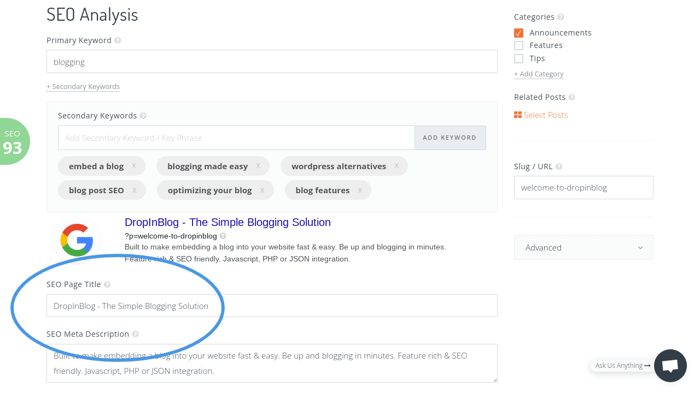
2. Meta Title and Description
Craft a compelling meta title that uses power words to good effect. Your meta title should be no more than 60 characters long and must include your target keyword for best results. Using a number in the title has also proven to be appealing to the eye and can increase the click-through rate.
The meta description doesn’t directly impact ranking but it is still helpful for SEO broadly. It also provides a brief summary of the content on the page to the reader. An ideal meta description will be between 140-160 characters and should contain the target keyword.
Search engines will only display the first 160 characters of a meta description; anything beyond that will not be visible and users won’t see it in their search results. In the image below, you can see that the meta description exceeds 160 characters, and the preview shows how the end of it will be cut off on the results page.
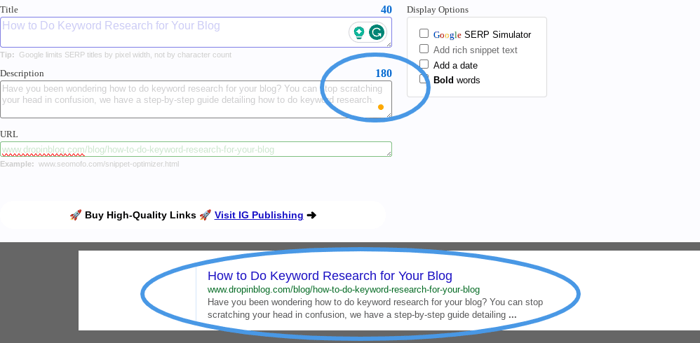
DropInBlog gives you the ability to add your own meta title and meta description, and it will even prompt you to include your target keyword.
3. Header Tags
Make sure your content is scannable to the reader by including headings and subheadings. The correct way to do this is by using header tags (H1, H2, H3). You should only use one H1 tag on your page, which is for the title. Other tags from H2 to H6 can be used as many times as you like and indicate different levels of subheading.
A page that is broken up by multiple subheadings will make it easier for the reader to absorb your content and to find specific information. It’s also a good way to target additional keywords, as text in the heading tags holds more weight according to the Google algorithm.
A proper heading structure helps AI-based search engines extract data from your content more easily. If you’re wondering why AI optimization matters, just look at the top of search results. Do you see links to websites within AI Overviews? Notice how visible these websites are. There’s your answer.
4. Image Optimization
Images should always be compressed, and you must also include image alt text for each image. This alt text explains the image in the event that it doesn’t display for some reason, but it also helps the image to be found in an image search – yet another way your content can be found online.
5. Content Quality and Relevance
Although there are many things that you optimize specifically for search engines, don’t forget that you are writing for humans. Always strive to write quality, unique content and not sacrifice quality for quantity – less is more, especially if your content is worth waiting for.
During the process of keyword research, you will begin to identify trending blog topics. Alternatively, you will see what topics are popular when completing a competitor analysis or from social media. By writing about topics that are relevant and inserting strong keywords, your content will draw traffic.
Another very basic way to ensure you develop quality content is in the writing itself. Structure your content well so that it grabs attention in the beginning and holds the readers' attention throughout.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is about the user experience. Website speed and performance optimization is the goal. Get started by running your website through an online performance tool like WebPageTest. Tools like this will scan your pages and identify any performance issues that need fixing.
6. Page Loading Speed
Page loading speed is one of the most important aspects of technical SEO. If your website loads slowly or has technical difficulties, then a user will exit quickly, resulting in what’s known as a high bounce rate. A high bounce rate is very bad for SEO.
One of the primary causes of slow page loading speeds is having too many large images on a page. All the images on your pages need to be compressed but try not to reduce the image quality at the same time.
Another common cause of slow pages is bloated unnecessary code. Where possible, try to minify code using a tool online that strips and cleans your code to remove any unnecessary extra characters. You can also use asynchronous loading for scripts to improve performance.
7. Site Structure and Responsiveness
Site structure and mobile responsiveness will greatly impact the user experience on your website. Map out all the pages of your site to understand how they connect and make sure they follow a logical hierarchy. The URL addresses should also follow a logical pattern that the user can understand. Avoid URLs like www.myblog.com/akdjj?j23 because this makes no logical sense; instead, an ideal URL would be www.myblog.com/blog/what-is-seo.
All websites today should be mobile responsive – if your website doesn’t load properly on a mobile device, you’re likely to lose readers. Some website builders have themes that are mobile responsive out of the box, but not all are. So, you need to double-check this and ensure you adapt the mobile version of your pages manually if needed.
8. Submit an XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a digital explanation of all the website pages you want indexed by search engines. This will also provide additional information to help the search engine understand the content. While submitting a sitemap is not essential, it does speed up the process of indexing, which is a good thing.
9. Add Schema Markup
For enhanced search results, it’s worthwhile adding schema markup to your pages. Schema markup is an easy-to-understand digital language that, again, just makes it easier for search engines to read and understand your content. It also allows you to create rich snippets of your content to display things like ratings, available stock, or prices. A little bonus is that DropInBlog automatically applies schema markup to all your blog pages.
10. Site Security
A secure site is a trustworthy site. Whether you have a checkout on your website or not, site visitors don’t like using unsecured sites. Get an SSL certificate and secure website protocols or risk losing visitors.
Additional Extras for an SEO Boost
There are a few extra things you can do that will provide a valuable SEO boost to your site. Firstly, sharing your posts across a variety of social media platforms is great for visibility and SEO. Make sure your website has a social media presence and include social sharing buttons on your pages so other people can share their favorite posts.
If you intend to target a specific locality, you should include relevant local keywords. For example, hiking tents in Wales if you want to attract leads with a particular interest in tents that are available in Wales. You can drill down when doing your keyword research to find out the best keywords by locality. Just keep in mind that most keyword research tools won’t let you investigate further than state or country without a paid subscription. In addition, if your business has a physical presence, don’t forget to add a Google My Business (GMB) listing and keep it up-to-date.
SEO Tools to Use
If you’re going to be doing your own SEO you need to audit your site before and after making changes. By analyzing your site at the beginning, you’ll get pointers on where to start the SEO-optimization process. A site audit after will show the improvements have taken effect and are either resolved or still need some work.
Some of the recommended tools available online both for free and with a paid subscription include:
- SE Ranking – Not free, but there is a free trial.
- Ahrefs – Sign up for free and get limited access to the site audit tool.
- SEMrush – Not free, but very popular and robust if you have the budget.
- GTMetrix – A free site speed audit tool.
- SEO Site Checkup – Provides a fairly thorough SEO audit; however, you have to sign up for access to the report.
- Page Speed Insights – Simple but thorough site audit and completely free.
Ongoing Monitoring
Using an analytics tool with your website will help you monitor the traffic your site is attracting. Google Analytics is one of the most popular and will show you trends, spikes, or when there’s a drop in traffic. You can check which pages are driving the most organic traffic and which keywords are bringing visitors to those pages and access your click-through rates (CTR) and bounce rates. The CTR can often indicate which meta titles are more appealing and a high bounce rate could be a sign there’s a page performance problem.
An analytics tool will also help you monitor conversion rates and visitor engagement with any call-to-action you have on the page. But, above all, monitoring your site performance helps you stay on top of the SEO changes you’ve made. If it’s working, great; if not, you can make some adjustments.
FAQs
Can I do SEO myself without any experience?
It is possible to do SEO yourself without any prior experience. Many individuals and small businesses with limited resources and knowledge of digital marketing have successfully learned and implemented SEO strategies.
What are some common mistakes when doing SEO yourself?
It’s very common to make a few mistakes when doing SEO yourself. The most common mistakes include:
- Keyword stuffing – cramming so many keywords into your copy that it ends up sounding unnatural. Insert keywords as naturally as possible and don’t overdo it.
- Forgetting to make your pages mobile-responsive.
- Not paying attention to technical SEO.
- Failing to monitor and make changes as needed.
What are the best resources for learning SEO?
There are a range of fantastic courses available online for learning SEO from the experts. The most reputable include Ahrefs SEO course, Neil Patel’s SEO Unlocked, or the SEMrush Academy – many of which are free. You can also opt to learn in a less formal way with resources like Moz’s Beginners Guide to SEO.
Final Thoughts
Hopefully, we’ve made it loud and clear that you do not need to be an expert to boost your SEO. You can learn how to do your own SEO – and you don’t even need to pay for a course because there are plenty of free learning resources available online.
The main thing to remember is to work through the optimization process step by step and be consistent. Keep a checklist or spreadsheet of the priorities for each page so you know what needs to be done and what changes you have already made. And, most importantly, monitor the changes. This means you’ll be able to quickly make adjustments, but it will also give you a confidence boost to see your efforts paying off. Good luck!





