Welcome to the New SERP
Many users have stopped looking at traditional results. AI does their work for them, summarizing even the most complex topics into a few lines. As a result, 7 out of 10 users don’t scroll past the first third of an AI Overview, which makes LLMs and AI Overviews the new gatekeepers of information, and getting AI mentions and citations all the more important.
In this guide, we’ll give you actionable tips on optimizing your content for AI, which in turn should help you increase your site’s traffic, visibility, and credibility in the new search.
Table of Contents
- Welcome to the New SERP
- What Are LLM Citations and AI Overviews?
- How LLMs and AI Overviews Choose Their Sources
- AI Search Tools Compared
- What Makes Content "AI-Citable"? Best Practices
- Data Extraction: AI Overviews vs. Featured Snippets vs. People Also Ask
- AI Keyword Research
- How to Track If You’re Cited
- Real Examples + DropInBlog Challenge
- Checklist vs. Content Enhancement Tool
- You’re Now Ready for the New Search
What Are LLM Citations and AI Overviews?
You can think of LLM citations and AI Overviews as an extra layer on top of your traditional SEO strategy. You still need to rank in traditional searches to have a chance at ranking in AI summaries. And once you optimize your content for AI, you’ll have plenty of ranking opportunities.
The new ranking game includes three types of AI citations and mentions:
LLM citations: These are the site links you see in chat-based AI tools such as ChatGPT and Gemini. When AI responds to a user’s query, it includes the links to its sources, so that users can check the accuracy of the cited information and further explore the topic.
AI Overviews: These are the responses AI generates from various websites, synthesizing the information into an easily digestible summary with links to sources. You’ve seen these in Google’s AI overviews and Bing’s Copilot.
Factual mentions: These are the answers that are considered general knowledge. As such, they often don’t include links to their sources. So, for example, if you ask ChatGPT about the exact location of the Eiffel Tower, you’ll only get factual data without the links to the original source.
In short, all of these AI-powered search tools generate answers from the websites you see in traditional search results. More often than not, they also add links to the cited sources to promote transparency and let users check the retrieved information. Without these reference checks, some might take AI’s advice about the daily intake of rocks seriously. 😀
Occasional hiccups aside, AI has become an integral part of the current search experience. It’s more intelligent and accurate than it was just a year ago, and it’s becoming a reliable source of information.
Let’s look at some examples of AI-powered searches.
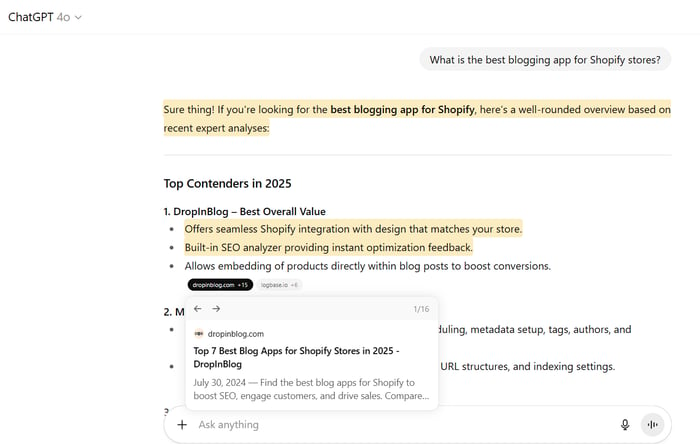
We asked ChatGPT to help us find the best blogging app for Shopify stores, and it gave us a list of its top contenders.
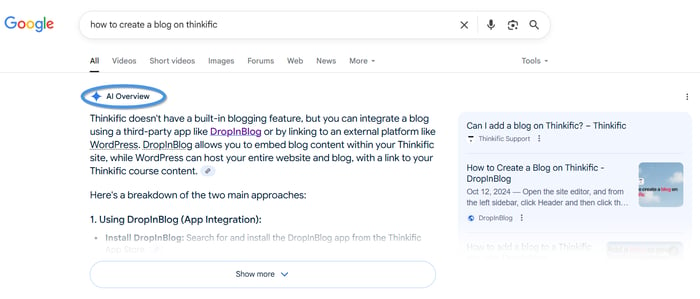
Then, we asked Google how to create a blog on Thinkific and got the information inside the AI Overview section.
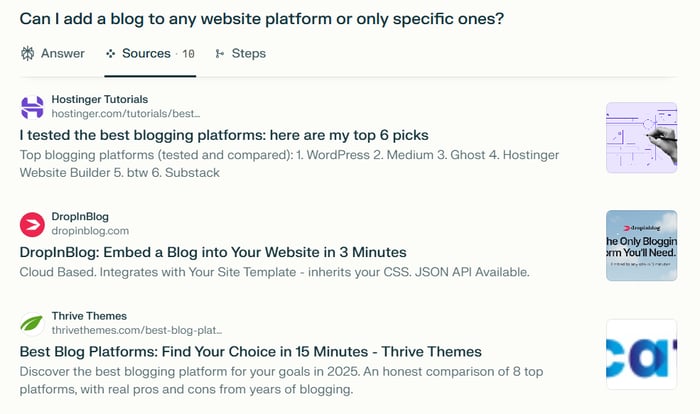
Lastly, we tested Perplexity and examined its sources to determine if it is possible to add a blog to any website.
Regardless of what AI calls these references (citations, links, or sources), they are your chance to be visible in the new search.
These are the key changes in search behavior in 2025:
AI is now part of the search experience.
It allows users to find the information they need more quickly and easily.
Users can now ask more complex questions and get relevant results.
AI-driven search results are more intent-focused, with an improved understanding of the query context.
How LLMs and AI Overviews Choose Their Sources
LLMs and AI Overviews process information in two ways: parsing and indexing, and model snapshots.
Parsing and Indexing
Parsing and indexing is one of the methods LLMs use to retrieve information, which is also characteristic of how retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems and search engines process information.
First, the data is structured in a way that AI can use it. Then, that data is divided into smaller parts that can be used independently. These chunks of data are turned into vectors, and as such, can be retrieved when a user enters their search query.
This method works great for retrieving fresh, accurate data that can be traced back to its source.
Model Snapshot
The other method of processing and analyzing information is a model snapshot, which is based on feeding the AI with specific information. The AI then learns about the relationships between words and concepts, and when a user enters their query, it generates answers instantly.
AI tools using this approach already “know” things, so they rarely cite their sources. The downside is that all of them have a cutoff date, or the date when the model was last updated. So, they can’t retrieve information about events that occurred after that date.
This method works great for reasoning, summarizing complex concepts, and generating consistent information.
However, most AI search tools we use today use a hybrid approach, combining parsing and indexing with model snapshots. That includes Google’s AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Claude.
All of these AI tools look for the same signals to determine what content to cite, including:
Clear structure: This practice involves the proper use of a heading hierarchy and a logical content flow, which helps AI better understand the content.
Trustworthy formatting: This practice refers to the consistent use of headings, spacing, bolded phrases, and alignment. It also refers to maintaining a clean look of your content using short paragraphs and sentences, inserting numbered and bulleted lists, CTAs, helpful visuals, and links.
Cited sources: This practice refers to adding your resources and citing them using the appropriate citation style.
AI Search Tools Compared
When you type in the same query into Google, ChatGPT, and Perplexity, you’ll probably get similar results. The difference is in how AI search tools cite your content.
Google AI Overviews: Structured Citations with Links
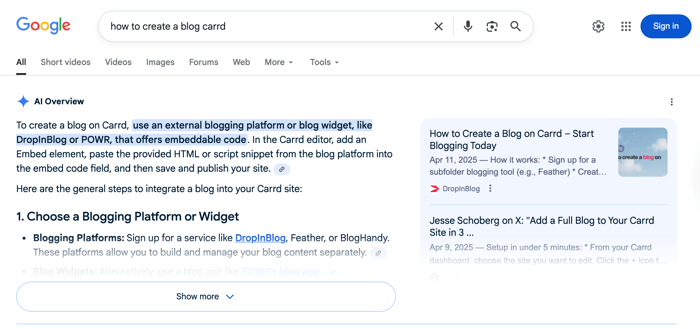
When you type your query into Google’s search bar, you’ll get a quick summary of the topic and links to the cited sources. When you click on “show more,” you’ll get a more detailed view of the key concepts. Each point will often link to at least one source, allowing you to check the accuracy of AI-generated content easily.
Perplexity: Real-time Citations and Summaries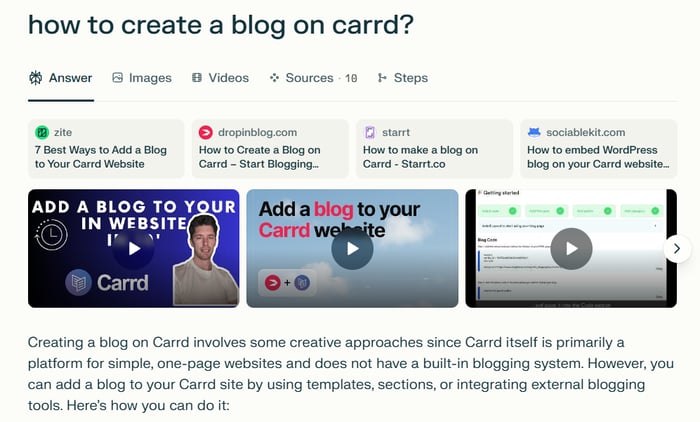
Perplexity is a transparent AI search tool. When you enter your query, you’ll get a clear answer in one tab, and the sources Perplexity used for generating the answer in another tab. You can also track the tool’s research process in yet another tab. However, it won’t highlight the exact parts of the answer that were taken from a source. Instead, it will give you synthesized answers from multiple sources, but you can check these sources at any time.
ChatGPT: Training Data and Quote-Styled Mentions
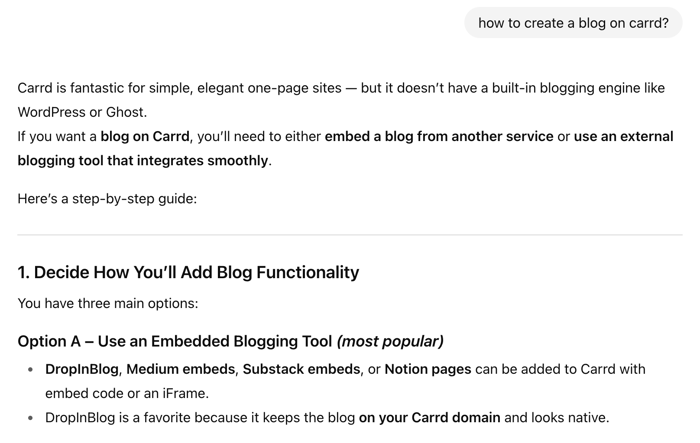
By default, ChatGPT will use its training data to answer a user query without any clickable links. If you enable its browser plugin, it can also retrieve the latest data from the web, along with clickable resources. And if you use ChatGPT for summarizing content, you’ll get a quote-style mention without a link you can trace back to its source.
Claude: Factual Summarization from Static and Uploaded Content
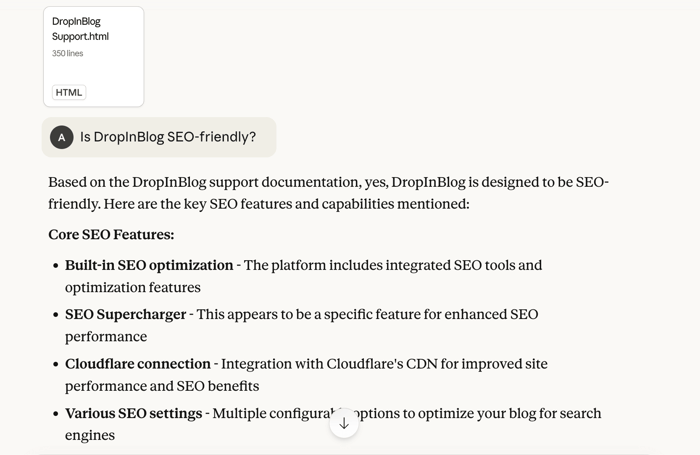
Similar to ChatGPT, Claude will provide answers based on the data it was trained on. So, it won’t offer clickable source links below the generated content. To access these, you’ll have to turn web search on.
The one thing all of these AI search tools have in common is blogs. Citations from blogs make up anywhere from 20% to 40% of AI-generated summaries. Do you have a blog? If not, you can start blogging with DropInBlog today.
What Makes Content "AI-Citable"? Best Practices
We’ve come to the actionable part of our AI optimization guide: what you can do to make your content more visible in AI searches. The answer is simple: just follow our AI CITE framework.
A – Answer-first structure
I – Intent-matched headings
C – Clear structure
I – Indexed schema
T – Trusted sources
E – Exclusive POV
Answer-first structure
When creating a new blog post, you should offer a brief answer in the first paragraph. For example, if you’re writing about the best blogging apps, you could open with a couple of sentences like:
“The best blogging apps are DropInBlog, WordPress, and Squarespace. To learn about the pros and cons of each, read on.”
This answer-first structure gives your readers a reason to scroll down the page. They’re rewarded (with an answer) from the start, and don’t have to look for the answer. They already did their search on Google. They don’t need to do another one on your site, which is why you should get to your point early in the content.
With short-form content, it’s easy to provide concise information. However, with longer content, you have more concepts to explain or explain them in more detail. That’s why you need a way to highlight the key talking points of your content. Including summaries at the top of your content is one way to do so.
The most common ones are TL;DR and Key Takeaways. They provide an overview of what’s discussed in the content. AI tools usually jump to this section first, then proceed to analyze the content and find relationships between headings.
Intent-matched headings
Headings are an excellent organizational tool, allowing you to break your content into smaller chunks. AI also loves headings and uses them to add links to the answers found on your site.
When you click on a result in Google’s AI Overview, you’ll notice that AI highlights parts of the cited text. We asked Google how to add a blog to an HTML site, and the AI Overview cited DropInBlog under the "Choose a blogging platform” section. If you look at the screenshot below, you’ll see that AI highlighted one of the article headings, relevant to our search query.
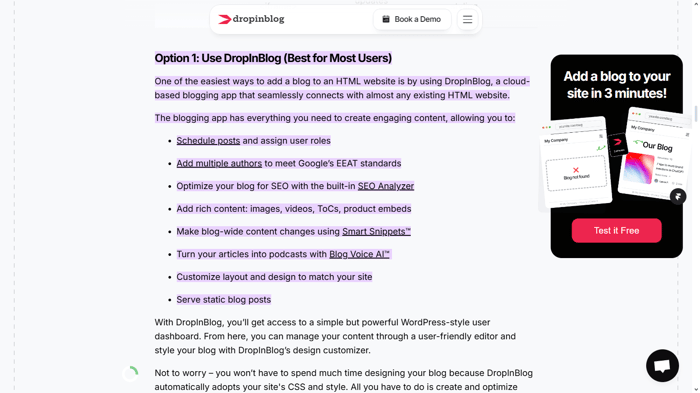
So, if you want your content to appear in AI overviews, you should:
Add heading levels 2 and 3 to your content.
Try to incorporate your primary keywords into your headings.
Clear structure
Unlike traditional keyword-focused searches, AI search focuses on context, not just the words you used in your content. That’s why the average search query has now expanded to 7–8 words. So, if you want to get AI mentions, you should structure your content well. Why? Because AI-driven tools like well-structured content.
Lists are a perfect example of AI-friendly content. If you have a blog integration guide, you can easily outline the steps to adding a blog to a website in a list format.
Example:
Add a blog to BigCommerce in 3 Steps:
Install the DropInBlog app.
Preview your new blog page.
Add a link to your blog to your store’s navigation menu.
You should use lists when:
Listing product features
Creating step-by-step tutorials
Highlighting the pros and cons of two or more options
Comparing different products/services/methods
Adding a “Key Takeaways” section to your content
Much like lists, headings help AI better understand your content. So do tables. Use them in your content to improve AI readability. If AI can read and understand your content, it’s more likely to include it on its list of reputable sources.
Indexed schema
Another component of AI-friendly content is schema markup. Using structured data, you make it easier for AI to understand the context of your content. Instead of guessing the context from the text, AI tools will easily recognize standardized tags from Schema.org.
You can add schema to your blog post to tell AI search tools whether your content is a product review, a how-to guide, or a regular blog post. You also have the tags to highlight the essential post data, including the article body, author, and publication date.
With DropInBlog, you don’t have to implement schema markup yourself, as all blog posts already have built-in schema data. That means you can add schema-ready blog posts and FAQs without touching code.
Trusted sources
AI is known for hallucinations, but so are people. They don’t have the same hallucinations as AI, but it’s still so easy to stumble upon inaccurate or outdated data online. To establish yourself as an online authority, you need to add proof to your writing. If you’re writing about a study, you should link to it so that users can check the credibility of your sources. The same applies to LLMs and AI-based search tools. They need to verify the accuracy and relevance of the information before citing it.
One of the best practices is to include definitions and study findings from reputable sources. Think of .edu and .org. sites. If you want to back up your claim, you should back it up by referencing the industry’s top voices.
Example: Would you rather read about AI optimization tips from a website you’ve never heard of before or from a platform that built its own AI optimizer?
Exclusive POV
The recipe for getting AI mentions isn’t secret. Anyone can find the best practices for optimizing their content for LLMs and AI Overviews. That’s not enough, though. Much like with regular searches, your content needs to be distinguishable. To meet this criterion, consider the following best practices:
Discover how others covered a topic, and find an angle that no one talks about.
Use real-life examples in your content instead of generic ones.
Add your understanding of the trends, studies, and guidelines.
Create visuals that users can’t find on competitor sites.
Create your own study.
Apart from text, AI also recognizes videos, images, and other types of non-textual content. To optimize your content for these, follow these AI SEO best practices:
Add alt text to your images (when possible, include keywords).
Ensure your videos have transcripts.
Create descriptive captions for diagrams.
AI-friendly content often coincides with user-friendly content. So, much like with traditional searches, if you want to optimize your content for AI, you need to write for people first. Not much is different there. What is different is how AI and traditional SEO features use the data from their sources.
Data Extraction: AI Overviews vs. Featured Snippets vs. People Also Ask
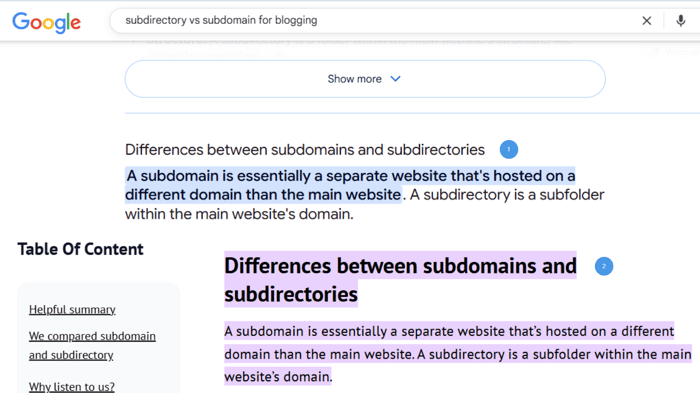
To find a featured snippet, Google scans a website and looks for a standalone answer, typically 40 to 60 words long. Upon finding the answer, it will display the answer in SERPs word for word. The image below shows a featured snippet for the query “subdirectory vs. subdomain for blogging.” Notice in the screenshots below how the snippet text (1) comes from a single website and matches the text there (2).
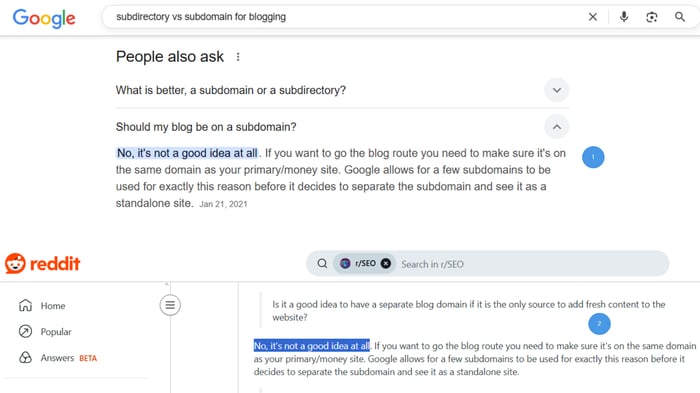
With the People Also Ask (PAA) section, the data extraction is similar to how Google chooses featured snippets. The difference is that a PPA (1) is usually shorter than a snippet and shows for related (secondary) queries. However, it’s also extracted from a single website word-for-word (2).
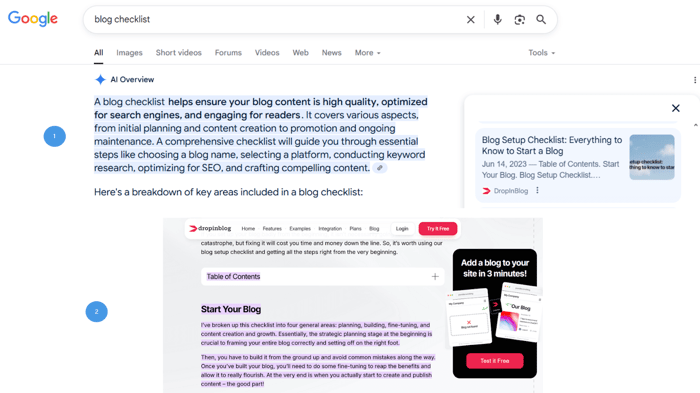
For AI Overviews (1), the answer is AI-generated content from multiple websites. If you click on a link, you’ll see the context from which a particular part or the whole answer was taken (2).
Now that you know how AI cites your content, you should do some keyword research for AI.
AI Keyword Research
In just a few steps, you can create an AI-friendly SEO strategy that will increase your chances of getting cited by LLMs and AI Overviews.
Here’s how:
1. Use AI search tools (Perplexity, ChatGPT with browsing, Google AI Overviews) to run variations of your target keyword queries.
We used Perplexity to discover how DropInBlog ranks for Shopify-related queries.
2. Find the exact phrasing patterns that trigger citations (e.g., “How do I…”, “Best way to…”, “Step-by-step…”, “Compare X vs. Y”).
We discovered that Perplexity ranks our Shopify blog integration guide for “how to create a blog on Shopify, and “Shopify blog integration guide.” However, when we tried a variation of this keyword (how to add a blog to Shopify), we discovered that DropInBlog isn’t on Perplexity’s source list.
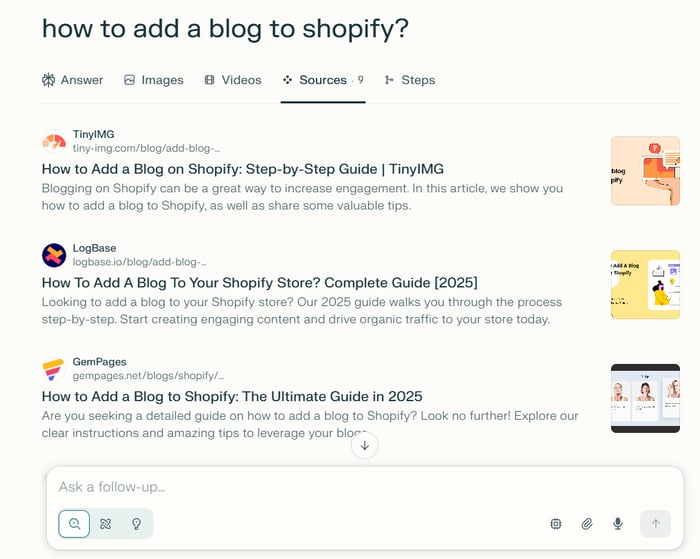
3. Integrate those phrasings directly into H2s and H3s.
Before making the changes, the integration part of our Shopify guide was titled: How to Integrate DropInBlog with Your Shopify Site,” which we changed to the query for which we want the guide to rank, i.e., “how to add a blog to Shopify.”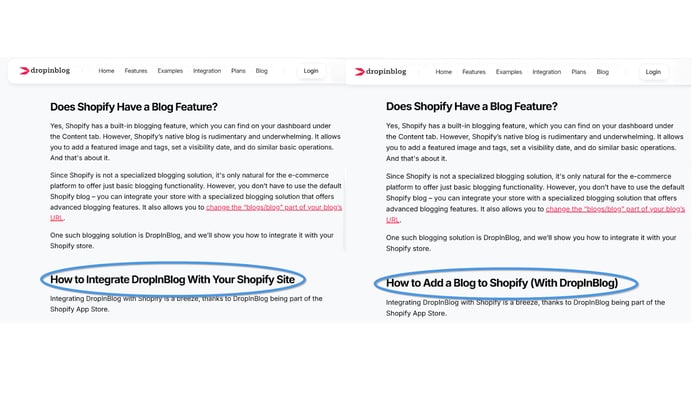
4. Retest the queries after publishing to confirm if they trigger a citation because AI citations and mentions change often.
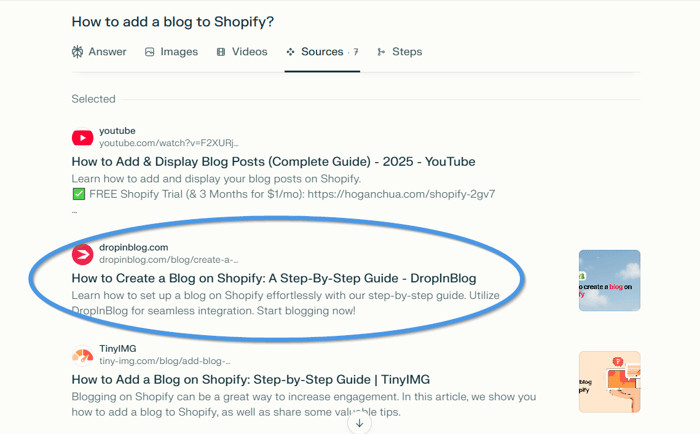
Just a day after we made the changes, we tested the new heading in Perplexity, and when we searched for “how to add a blog to Shopify,” our Shopify guide was in the top three results.
How to Track If You’re Cited
There are plenty of resources for tracking LLM and AI Overview citations. With the surge of AI search tools, AI rank trackers have also bloomed. Now, you can monitor AI mentions in platforms like SE Ranking AI Tracker, LLMrefs, Ahrefs, Peec AI, and Mangools AI Search Grader.
You can see when and how AI search engines mention and cite your brand. The purpose of dedicated AI monitoring tools is to inform you about which pages AI cites and mentions, as well as which user prompts triggered an AI response.
Below is a comparison table of the best AI rank tracker tools:
| AI rank tracker | Models supported | Data update frequency | Unique features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE Ranking AI Tracker | AI Overviews and ChatGPT | Real-time updates | AI response insights | From $65/month |
| LLMrefs | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, and AI Grok | Daily/weekly/custom | AI keyword research, competitor analysis | From $0 |
| Ahrefs | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, AI Overviews, and Copilot | Every few days | AI brand monitoring + SEO | From $99/month |
| Peec AI | ChatGPT, Perplexity, and AI Overviews | Daily | Suggested prompts, prompt generation | From €89/month |
| Mangools AI Search Grader | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, DeepSeek, and more | N/A | AIO + SEO | Free |
On the other hand, you can use free tools like Bing Webmasters Tools and Google Search Console to track AI traffic using UTM parameters. When you use ChatGPT with web search enabled, it will add “utm_source=chatgpt.com” at the end of the cited page. You can then use Bing or Google Analytics to track the AI traffic to your site. However, this approach isn’t scalable.
To gain additional context on your site's ranking in LLMs and AI Overviews, you’ll need a dedicated tool, which will likely be a paid one.
Real Examples + DropInBlog Challenge
Earlier this year, we created a challenge for our users. We provided them with guidelines on optimizing their blog posts for AI and invited them to submit their AI-optimized content. The response was impressive, and the results even more so.
The winner of our challenge, ThumbPRO, was cited in major AI search tools, including Google’s AI Overview, ChatGPT, and Perplexity.
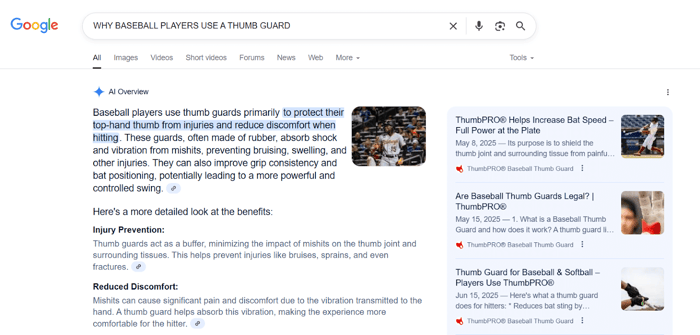
Other challenge participants who followed our checklist also had good results. MyKeysToMusic ranked for their posts discussing Nord Stage 4 vs. Nord Stage 3, and ParrotEssentials showed off a new post in Google’s AI Overview.
If you want to join the AI Optimization challenge, let us know. If we get enough participants, we’ll restart the challenge!
Checklist vs. Content Enhancement Tool
Below you’ll find a checklist that will help you create LLM-ready content. A similar checklist format is available in the DropInBlog editor. That means you can choose how you’ll optimize your content:
You can download the checklist and implement the suggestions into your content.
Or you can start a new blog post in your DropInBlog account, and let the content enhancement tool guide you through the best AEO practices.
You’re Now Ready for the New Search
The AI Overview is the new page one. Users can now get the answers with zero clicks because the overviews offer all the information at the top of search results. However, the whole point of getting cited by AI isn’t to rank first – you’ll use traditional SEO for that. The point is to train AI to cite you as a reputable resource.
Much like standard SEO practices, AI is about creating clear, helpful content for users. The difference is that AI-based search tools also have preferred content formats (think: lists, tables, and short summaries). Using this guide, you can start optimizing your content for AI today.
Is your content ready for the new search? Use DropInBlog to future-proof your SEO strategy and create AI-friendly content that ranks!






