Comparing Magento to Shopify is not quite a straightforward affair. To a certain extent, it comes down to comparing e-commerce platforms that represent two different software models: open-source and SaaS. However, there’s much more to it than just this.
Magento is essentially open-source e-commerce software. Open-source software is free to download, install, use, redistribute, and modify. As with any other example of this type of software, the control, flexibility, and customizability it offers are its main strengths. These are great to have, but they come at the expense of simplicity and ease of use. One of the reasons why is that they require coding and tech-savviness.

Shopify is an SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) e-commerce platform. As such, it’s cloud-based and available for users via a monthly or annual subscription. It’s proprietary software that doesn’t require installation and is accessible through web browsers. It’s simple and easy to use and it doesn’t require coding skills. However, these advantages come at the cost of control, flexibility, and customizability (compared to Magento).
However, this is but a generalization of what Magento and Shopify actually are. That’s why we need to dive deep into the specifics of these two e-commerce software systems to better understand them and the scope of the possibilities they offer. Only then will we see that things are not as simple as they seem to be at first glance. So, without further ado, let’s start our Magento vs. Shopify comparison.
Table of Contents
Different Variants of Magento
Before anything else, we need to clarify one quite confusing side of Magento: the fact that this term is related to a few different entities:
- Magento Open Source
- Magento Commerce
- Adobe Commerce
Initially, there were two types of Magento: Magento Open Source and Magento Commerce. They were built on the same codebase, but the first was open-source and free while the second was proprietary and paid. Things started to get much more complex in 2018, when Adobe acquired Magento Commerce from its previous owner.
When Adobe bought Magento Commerce, Magento Open Source stayed intact, which didn’t come as a surprise at all. Magento Open Source is not owned by Adobe; as an open-source initiative, it relies on a large community of developers, users, and fans who contribute in different ways to this project.
In contrast, from the get-go Adobe’s idea was to fully integrate Magento Commerce with its own services and apps, or more accurately, into the products it offers in the Adobe Experience Cloud. Those include the Adobe Experience Manager Sites, Adobe Experience Manager Assets, Adobe Analytics, etc.
By April 21, 2021, this process came to completion and Adobe announced the new unified brand, Adobe Commerce (Adobe plus Magento Commerce). This means that now, when you search for Magento Commerce and open its official website, what you’ll actually see is Adobe Commerce:
The trouble stems from the somewhat confusing ways the term “Magento Commerce” is still being used. If you do some research, you’ll still find Adobe products that contain “Magento Commerce” in their names, such as Magento Commerce Pro On-premise and Magento Commerce Pro Cloud. To add to the confusion, if you browse through Magento Open Source vs. Magento Commerce searches, this will be one of the results you’ll find:
We’ll show the complete list of compared features later. For now, what’s interesting is that this comparison is on the official Adobe Commerce website, but it gives the impression that Magento Commerce is still a separate brand or offering, different from Adobe Commerce, which is not the case.
Let’s try to make sense out of all this seemingly conflicting information.
Magento Open Source
Magento Open Source is the version that anyone can download and use for free. It’s not owned by Adobe. It comes with certain built-in e-commerce functions, but you need to buy hosting to publish your e-commerce site on the web.
Despite being free to use, it can still cost you an arm and a leg to build and run a storefront on Magento Open Source. There are different estimations of the total costs, but overall, you’ll likely have to shell out somewhere between $15,000 and $50,000 for a nice fully functional e-commerce store that’s in line with your brand. That would include all the hosting, extension/integration, development, design, support, and maintenance costs.
Magento Commerce/Adobe Commerce
Magento Commerce is the e-commerce software that Adobe bought, integrated with the Adobe Experience Cloud, continued to develop further, and turned into Adobe Commerce. The huge advantage of Adobe Commerce is that now you can integrate this new product with other products from the Adobe Experience Cloud, such as the Adobe Experience Manager.
So, technically, Adobe Commerce is Magento Commerce. When you see a Magento Open Source vs. Magento Commerce comparison on the official Adobe Commerce site, in fact, this is a Magento Open Source vs. Adobe Commerce comparison.

Then why use the name “Magento Commerce” at all? Probably because this is a name known by everyone in the e-commerce niche, while the term “Adobe Commerce” might confuse users who don’t know about Adobe’s acquisition and transformation of Magento Commerce. For the very same reason, we’ll be using the term “Magento Commerce” throughout this article.
The Differences Between Magento Open Source and Magento/Adobe Commerce
The following table shows the key differences between Magento Commerce and Magento Open Source as far as built-in features, as well as advanced e-commerce functionalities, are concerned:
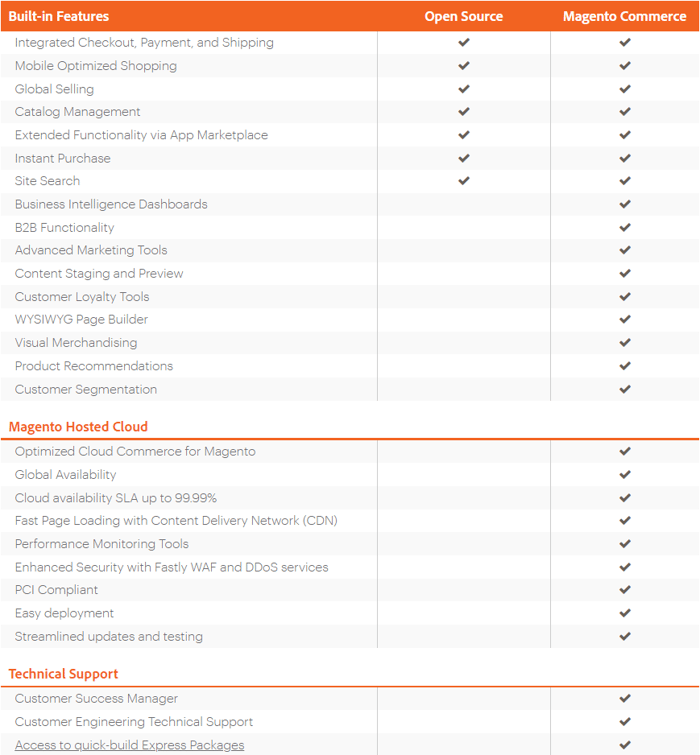
To mention a few obvious advantages of Magento Commerce, the WYSIWYG editor along with the web hosting can save you a ton of time and frazzled nerves. The B2B functionality together with the advanced marketing tools can help you raise your business to the next level. And don’t get us started on the importance of dedicated customer support that covers every single facet of your e-commerce store.
Magento Commerce Pro On-Premise
Magento Commerce Pro On-Premise is based on Magento Commerce, but, as its name suggests, it’s not a hosted solution. In Adobe’s documentation, you can also find references to “on-premises Adobe Commerce,” which due to the lack of first-hand experience with this offering, we assume is virtually the same as Magento Commerce On-Premise.
The on-premise offering is for businesses that want access to more out-of-the-box features (as well as integrations) than Magento Open Source offers, but they prefer to host their e-commerce store on company’s own servers rather than in the cloud or on a hosting provider’s servers. This can give them more control, but it's a maintenance-intensive and pretty expensive endeavor.
Speaking of expensive, the price of this and any other package that Adobe offers depends on your business’ yearly GMV (Gross Merchandise Value) and AOV (Average Order Value). It starts at around $20,000+/year and can go as high as $100,000+/year. However, keep in mind that this is just an approximation. For a specific price, you’ll have to contact Adobe.
Going back to Magento Commerce On-Premise, it’s essentially just another Adobe offering powered by Magento Commerce, and it’s now offered under the Adobe Commerce brand. However, it seems that since the launch of Adobe Commerce, Adobe’s recent tendency has been to emphasize its cloud e-commerce offering, which might eventually lead to a retirement of the on-premise project.
Magento Commerce Pro Cloud
Magento Commerce Pro Cloud is the opposite of the on-premise package. It’s a cloud-hosted solution, more technically described as PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service). PaaS is a cloud platform that provides everything that’s necessary to build, test, deploy, manage, and update web apps. You can access PaaS via a web browser.
Like the on-premise package, Magento Commerce Pro Cloud is now part of Adobe Commerce comprehensive toolkit. It provides the core Adobe Commerce features – like advanced reporting, guaranteed minimum of 99.99% uptime, Commerce Integration Framework, production, staging, and development environments, etc. – with the possibility for businesses to upgrade by, say, buying on-demand business intelligence services (on top of the core ones) available on the Adobe Commerce platform.
We hope that this short overview of the naming confusion related to Magento cleared things up. If it didn’t, perhaps our insight into the features will. But, more on that later. Now, let’s take a look at Shopify and see if their structure is just as confusing.
Two Types of Shopify?
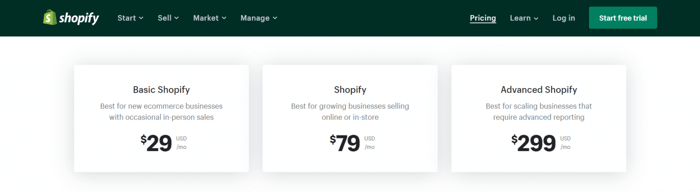
It’s not quite the same complex animal as Magento, but it can be argued that there are two types of Shopify as well: standard Shopify and Shopify Plus. The standard Shopify is what the majority of people mean when they refer to the e-commerce platform we all know and love. The following image shows the three standard Shopify pricing plans:
Shopify Plus, on the other hand, is an enterprise-level offering by the Shopify company. It includes everything from the most advanced standard Shopify plan plus a lot more options. It caters mostly to large and high-volume businesses.
Shopify Plus starts at $2,000/month, but it can go much higher depending on your business and the custom implementations you choose to have.
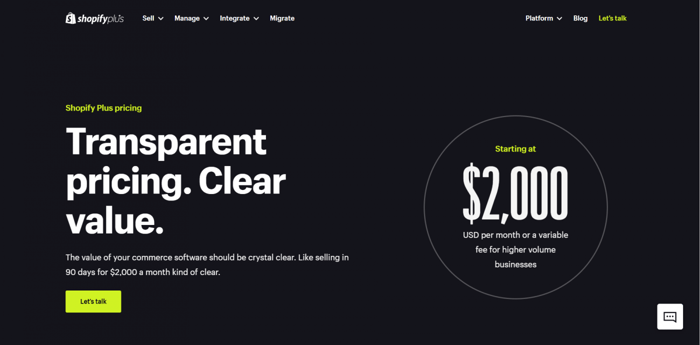
The following is a list of some key features unique to Shopify Plus:
- Optimized and customizable checkouts
- B2B functionality
- Advanced scheduling and automation apps like Launchpad and Shopify Flow
- A wholesale channel (your own store) and selling in two places (Shopify’s Handshaker marketplace)
- Short chunks of code called Shopify Scripts that take store customization to the next level
- More API calls
- Merchant success program
- Shopify Plus Academy
Comparing the standard Shopify to Magento Commerce is not quite fair. Its pricing and features tell a very different story from the one told by Magento Commerce. Unlike the standard Shopify platform, the latter caters primarily to enterprise-level and large businesses.
Shopify Plus, by contrast, is Shopify’s answer to Magento Commerce. As you’ll see in the next sections, in many cases it makes much more sense to compare Magento Commerce to Shopify Plus rather than to the regular Shopify platform.
Why Use Magento?
Magento Is Applicable to a Wide Range of Businesses
As some other reviewers also suggest, Magento can be a good e-commerce solution for someone who runs a business in a niche that includes goods related to sensitive or contentious topics. One example of a business of this type is selling weapons or products that involve cannabis.
In this particular case, when we say Magento, we mean primarily Magento Open Source. The main reason why it could work in this scenario is that as free-to-use software, it doesn’t enforce restrictive policies and terms of use. In contrast, Shopify has official rules that you have to play by to run your business on the platform. For instance, you might want to sell products that the company doesn’t allow.
Control, Flexibility, and Customizability
This is something you’ll hear over and over again about Magento Open Source (as well as other open-source platforms). Having complete access to the code is sufficient in itself to show you the level of creative control, flexibility, and customizability that has been granted.
Clearly, this means that in order to build the exact storefront you imagined, you need to use code extensively. As we mentioned earlier, this implies that you have to set a budget for a developer or team of developers and possibly even designers. Costs can add up over time, but if you choose Magento, there’s hardly any other way to build that highly customized e-commerce store.
B2B
It can be said without any exaggeration that B2B is one of the areas where Magento Commerce really shines. Since in B2B commerce you deal with other companies, which means demanding logistics requirements, highly advanced and effective tools are a must. What B2B features does Magento Commerce offer? Here’s a fraction of the things you can do:
- Create company accounts with buyers classified into different categories.
- Set automated approval of orders.
- Configure different levels of buyer access and permissions.
- Save shopping lists to speed up recurring sales.
- Customize pricing and catalogs according to your clients.
- Create a personalized user experience with each site visit (a proven technique to improve conversion rates).
- Build e-commerce sites optimized for mobile devices.
- Make vast use of advanced business intelligence and reporting tools to better understand customers and your own business, and so much more.
Complex and Scalable Businesses
Essentially, Magento is extremely flexible and powerful open-source software, regardless of the version you use. For instance, Magento Commerce is basically the open-source Magento software on top of which are built additional functionalities.
As such, Magento has limitless potential. It can meet the needs and requirements of even the most complex and demanding businesses. Expertly used, it allows big and fast-growing companies to create custom advanced and convenient solutions for their e-commerce businesses.
Cutting-Edge Technologies: Headless Commerce and Progressive Web Apps
Headless commerce and progressive web apps are at the forefront of today’s high technology.
By uncoupling a store’s front-end from its back-end (headless commerce), Magento Commerce creates more possibilities for building new convenient front-end solutions. Changes on the front-end, which create a richer and personalized user experience, become possible without modifications on the back-end of your store. This saves you time and money and leaves a lot more room for experimentation and innovation.
PWAs (progressive web apps) are a pretty recent innovation. They combine the features of both native as well as web apps. Native apps are applications that you need to install on your devices to use them while web apps do not require installation. They’re accessed through web browsers. Both have advantages and disadvantages.
PWAs try to bridge the gap between these two categories. Several years ago, it was unimaginable for a web app to work offline, but PWAs made this possible. In addition to the offline access, they look and act much more like any other app that you install on your desktop or mobile phone. They’re built to be more secure thanks to minimal communication with the internet.
The mere fact that PWAs don’t require an internet connection to work is sufficient to show how useful they can be in the e-commerce context. That’s why Magento Commerce has developed a feature called PWA Studio, which is a powerful suite of tools that enable its customers to build PWAs and take advantage of this state-of-the-art technology.
Why Use Shopify?
You Can Do It Yourself
With Shopify, you don’t depend on developers and designers, especially on the lower-tier plans. This may not be the case with Shopify Plus and perhaps not every Shopify merchant, but generally speaking it’s true.
The whole point of Shopify is for everyone to be able to build and run an e-commerce store, without exception. Hence, the high level of abstraction and simplicity of its software. Unlike Magento, where for the most part you depend on code and professional help in the fields of development and design, Shopify gives you everything you need to get your store off the ground and start selling in no time without coding and professional assistance.
Easy to Extend
When it comes to extensibility, Shopify may not offer the high level of extensibility found in Magento, but it’s a far cry from a limited platform. Moreover, Shopify makes extending the range of your store’s functionalities a breeze. With a vast ecosystem of apps available in the Shopify App Store, you can add any new functionality you want in a matter of seconds. The good news is that a large portion of these extensions are free or include a free plan.

With hundreds of available integrations divided into nine main categories that branch out in a ton of subcategories, the chances are slim that you won’t find what you need or want. The best part is that enjoying the perks of the Shopify integrations is just a few clicks away.
Say you need a blogging app (and why wouldn’t you, considering how invaluable a sales and marketing tool a blog can be?). You just head over to the Shopify App Store, find an awesome blogging app like DropInBlog, click “Add app,” and you’re well on your way to blogging. That’s how simple it is.
Overall, there’s hardly any aspect of Magento that can match the simplicity of Shopify, including how simple it is to integrate new uber-cool and useful functionalities.
Maintenance
A Magento store is an ongoing, never-ending project in the strongest sense of the word. It’s not that you build your Shopify site and you’re done, once and for all. But running and maintaining your Shopify store is a fairly mundane task, and the same can’t be said about Magento. Magento is maintenance-intensive and keeping a Magento site running smoothly can be a challenging and laborious task.
Just one example will suffice. While on Shopify software updates are literally none of your concern, on Magento you have to take care of the updates and constantly be on watch in case an update creates software conflicts and breaks something inside your e-commerce system.
Ease of Use
You might’ve already noticed, but it seems that everything we’ve said so far revolves around one recurring theme – ease of use. It runs through all three previous Shopify topics. Undoubtedly, ease of use is one of the biggest pros of the standard Shopify, especially in the context of a Shopify vs. Magento comparison.
With Shopify, even zero coding experience and technical knowledge would not affect your e-commerce venture in any way. The visual editor, virtually non-existent maintenance (as far as your direct involvement is concerned), out-of-the-box fast and secure hosting (as opposed to Magento Open Source), available pre-built designs, and many other facets of the platform make running a Shopify store a thoroughly enjoyable experience.
This is in sharp contrast to Magento, where coding and tech-savviness are inseparable from your day-to-day activities. It doesn’t have to be you that’s doing the coding and maintenance; you can always hire professionals. However, the trade-off is a dramatic increase in the costs of running your e-commerce business.
Price and Costs
This leads us to yet another reason why Shopify can be a good choice: price and total costs.
As you might expect, there are additional costs to using Shopify on top of the pricing plans that we already discussed, such as transaction fees, credit card fees, commercial or high-end integrations, premium themes, and more. However, all things considered, the standard Shopify is much more affordable than Magento (including Magento Open Source). One of the points of any SaaS e-commerce platform is to bring e-commerce closer to regular users and make it accessible for everyone, regardless of their budget.
Shopify Plus is a different story. However, taking into account that, similar to Magento Commerce, it’s geared toward highly developed, and large businesses, the steep price comes as no surprise.
Over and Out
We hope that this Magento vs. Shopify guide was a fun and informative read. We tried not to leave out anything that we considered to be thought-provoking. We wish you all the best with your e-commerce venture and we can’t wait to see which platform you choose to build your e-commerce project on.